AI demand forecasting software for every SKU-location in your supply chain
Crateflow is a demand forecasting software built for mid-market manufacturers and distributors. We use machine learning and AI technoliges to predict demand for every SKU and location, highlight forecast risks, and recommend planning actions so you improve service levels without inflating inventory.
Confidence intervals instead of point estimates, customer signals and automatic updates.

What Is Demand Forecasting Software?
Demand forecasting software is a tool that helps businesses predict future customer demand for their products or services using various algorithms and historical data to provide accurate predictions.
This is crucial for managing inventory, optimizing production, and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
The software can alert users to potential out-of-stock situations and seasonality trends. When you sign up for a demand planning software like Crateflow, the tool picks up things that your Excel doesn't and actually saves you from stockouts and going under-stocked.
Why Demand Forecasting Software Matters for Your Supply Chain
For businesses with many SKUs and irregular ordering patterns, demand forecasting software can handle sparse and hierarchical data. An AI-powered demand planning software assists supply chain and operations managers with:
Technical Insights
Demand forecasting tools utilize advanced statistical models and machine learning to provide accurate predictions for you.
Improved Decision Making
Accurate forecasts help you in better planning and resource allocation.
Inventory Optimization
By predicting demand accurately, you can avoid overstocking and understocking, reducing carrying costs and lost sales.
Sustainability & Reduced Waste
Accurate AI-driven forecasting minimizes the need for rush orders and excess inventory, which can be costly.
Why AI Demand Forecasting Is a Good Solution for Mid-Market Supply Chain Leaders
AI demand forecasting is a game-changer for mid-market supply chain leaders because it offers significant improvements in accuracy, efficiency, cost reduction, and freeing up working capital.
AI allows for simulating different demand scenarios, helping your supply chain prepare for potential disruptions.
How Crateflow’s AI Demand Planning Software Works
Our AI demand planning software basically does three things in a loop: understand what’s happening, predict what will happen, and tell you what to do about it, all at the SKU–location level, with humans still in control.
From Historical and Real-Time Data to Accurate Demand Forecasts
We pull together your key supply-chain data: historical orders and shipments, current inventory levels, lead times, promotions, and other operational signals.
From Demand Forecasts to Demand Planning and Inventory Optimization
Our AI models add external drivers such as commodity prices, inflation, and broader market trends, instead of relying only on past sales curves. This takes demand sensing and forecasts to a higher level and makes planning and decision making much easier and more confident in supply chain and inventory management.
Key Capabilities of Our Demand Forecasting Software
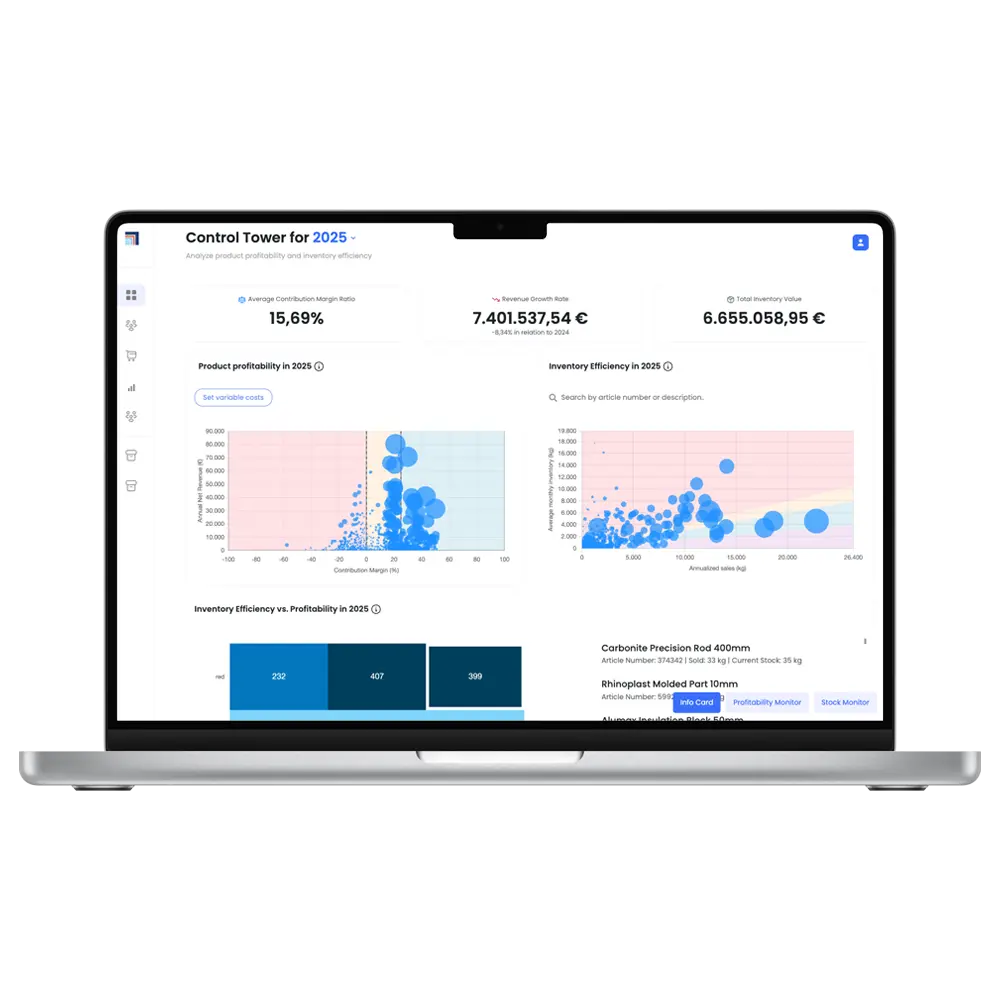
Granular AI forecasts per SKU and location
In Crateflow, our engine models every SKU at every location, not just at the aggregate level, and factors in seasonality, promotion behavior, and external drivers.
Real-time, ML-based demand updates
We use machine learning to generate precise demand forecasts and update them in real time as new data (orders, promotions, signals) comes in, so plans don’t rely on static monthly Excel runs.
Forecast uncertainty & confidence intervals, not just a single number
We explicitly model uncertainty with prediction/forecast intervals and confidence levels, showing confidence bands instead of a single point estimate and highlighting risk levels over the forecast horizon.
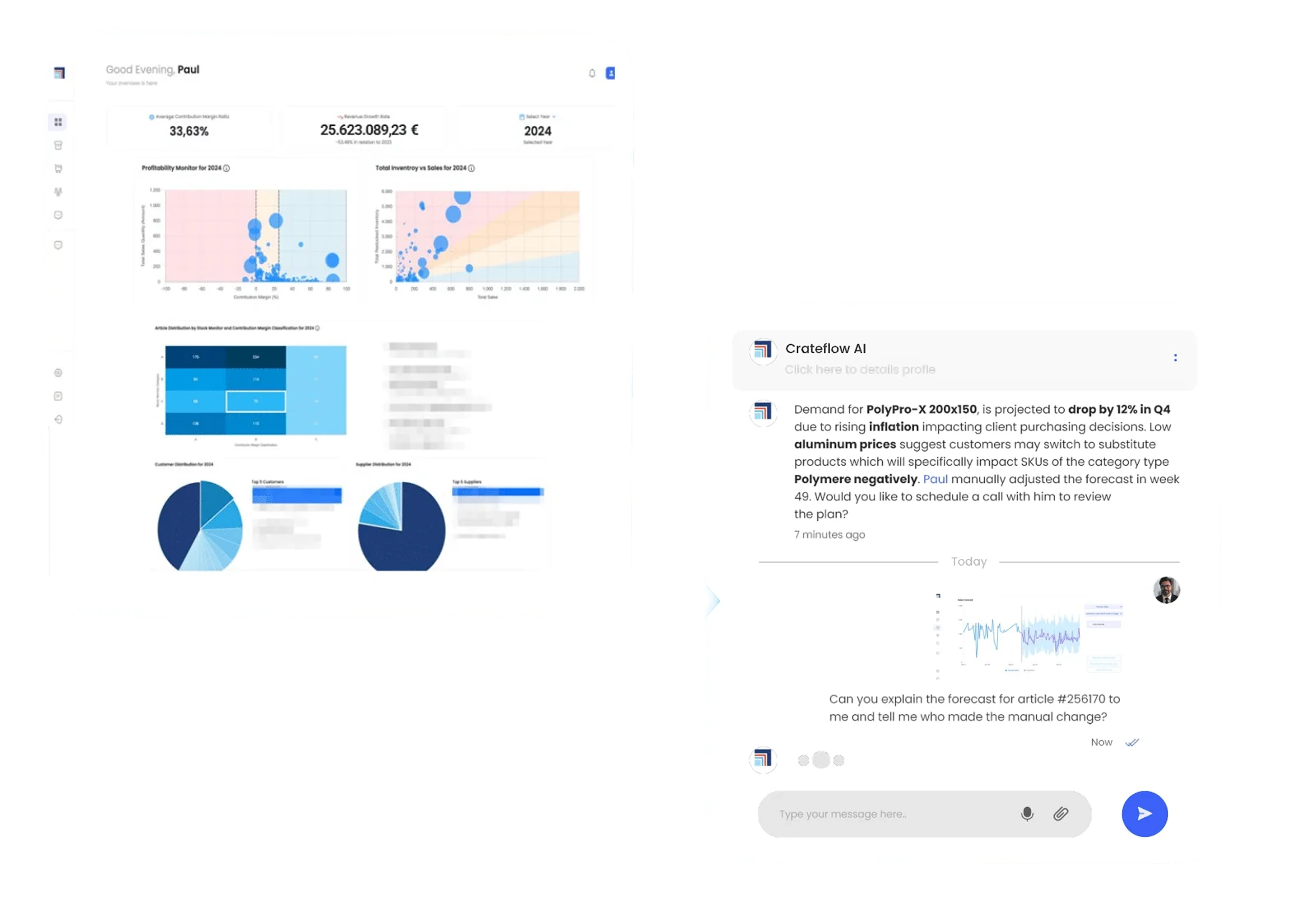
Customer signals, anomaly detection & trend flags
We surface customer signals, detected anomalies, trend indicators, and risk flags directly on the time series to make abnormal patterns visible without manual analysis.
Explainable AI via a “Control Tower” view
Our "Control Tower" consolidates financial and operational data and links it to forecasts, showing which factors (e.g., raw material prices, seasonal effects, inflation) are driving demand for each item, instead of a black box score.
Automated order suggestions & planning actions from the forecast
On top of demand forecasts, our platform generates automated order suggestions and supports replenishment using forecasted demand plus price, customer/supplier behavior, seasonal trends, and other signals as inputs.
Dynamic safety stocks & forecast-driven inventory optimization
Our forecasting feeds optimized safety stocks and dynamic, data-driven supply chain management to reduce both understock and overstock, tying forecasts directly to inventory policies instead of leaving them as “nice charts.”
Integration of ERP/CRM data and external signals
Our system is cloud-based and integrates with ERP and CRM systems while also pulling in external influencing factors such as customer trends, container freight rates, and world events into the forecast models.
Human-in-the-loop forecasting, not a fully autonomous black box
Our forecasts are adjustable by planners. The software provides intervals and explanations, while experts can still override or refine assumptions.
KPI-linked impact: inventory, cash flow, and service level
Our forecasting capabilities are tied to measurable outcomes: cases and product material cite up to 20–40% less inventory, 10–15% more free operating cash flow, and improved revenue and on-time delivery when forecasts drive decisions.
Business Outcomes: From Forecast Accuracy to a Smarter Optimized Inventory
AI-Driven Forecast Leads to Fewer Nasty Surprises
AI forecasting typically cuts forecast errors by 20–50% vs. traditional methods. This results in a cleaner demand signal, fewer last-minute corrections, and far less "buffer inventory just in case."
It Reduces Stockouts, Excess Inventory, and Lost Sales
Supply-chain analytics and AI forecasting can reduce product unavailability and stockouts by up to 50–65%, which translates into 2–3% revenue uplift for many consumer businesses, thanks to fewer missed sales.
It Improves Supply Chain Planning to Meet Customer Demand
Building production, purchasing, and allocation plans on AI-driven forecasts lets teams cut inventory by around 20–30% while improving service levels and reducing warehousing and administrative costs at the same time.
Getting Started With AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
Getting started with AI-powered demand forecasting doesn’t require a big IT project. You use the data you already have in your ERP/WMS and spreadsheets, and we guide you through a short, structured onboarding so you quickly see forecasts, order suggestions, and KPI improvements in one place.
Rollout in Your Existing Planning Processes
Share your operational data: export the relevant fields from your ERP, WMS, and planning spreadsheets (e.g., CSV/XLSX) and upload them. We merge these sources, clean them up, and highlight gaps or anomalies so the AI works on a reliable data foundation.
Map your current performance and KPIs
Next, we analyse your product portfolio, customer segments, and inventory situation: service levels, over- and under-stocking, capital tied up in stock, and typical bottlenecks. This gives you a clear baseline of how your demand and supply planning performs today.
Switch on the AI forecast and planning engine
On top of this baseline, machine-learning models generate demand forecasts and planning parameters. You receive concrete order suggestions that show their impact on service levels, inventory, and working capital.
Why classic forecasting fails
Volatility, variants, long lead times - with Excel as the bottleneck.
Volatile call-offs
Spikes & slumps derail plans.
Variant explosion
Many SKUs with little history.
Long lead times
Errors surface late.
Excel dilemma
High effort, low robustness.
Crateflow Forecast
More signals, less gut feeling.
AI-powered forecasts
Machine learning forecasts based on historical data.
Customer categorization
A/B/C customer segmentation by revenue and priority.
Order recommendations
Smart purchase suggestions based on demand forecasts.
Performance KPIs
Track forecast accuracy and business impact.
Product A
What improves
Availability
Fewer stockouts on A-items.
Working capital
Reduce excess systematically.
Speed
Noticeably less planning time.
Team focus
From firefighting to steering.
In 4 steps to live usage
Understand the data
Upload CSV/XLSX, define goals, align SKU groups & KPIs.
Train the model
Identify relevant signals, validate the model per SKU.
Test impact
First order recommendations in pilot - align with planners.
Go live
Rollout to production with monitoring, feedback & fine-tuning.
FAQ
FAQ: AI Demand Forecasting, Demand Planning, and Supply Chain Management
- Demand forecasting software helps businesses predict future customer demand for products or services. It uses historical data, statistical models, and sometimes machine learning to provide accurate predictions.
- AI demand forecasting leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and make highly accurate predictions.
- Demand forecasting software typically integrates with existing systems to pull historical sales data, market trends, seasonality, and other relevant factors. It then applies various algorithms to generate forecasts.
- Demand forecasting is about predicting future demand, while demand planning involves using these forecasts to make strategic decisions about inventory, production, and supply chain management.
- AI demand forecasting is much more accurate than traditional Excel-based methods due to its ability to handle complex data, seasonality, trends, and external factors.
- You typically need historical sales, POS, order, and shipment data, plus relevant exogenous variables like calendar effects and holidays.
- Most customers go from first data connection to a live, value-proven pilot in about 8–12 weeks, depending on data complexity and scope.